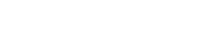Cognitive Fluctuations Enhanced Attention Network for Knowledge Tracing
We added flucKT into our pyKT package.
The link is here and the API is here.
Original paper can be found at Hou M, Li X, Guo T, et al. “Cognitive Fluctuations Enhanced Attention Network for Knowledge Tracing.” Proceedings of the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2025.
Title: Cognitive Fluctuations Enhanced Attention Network for Knowledge Tracing
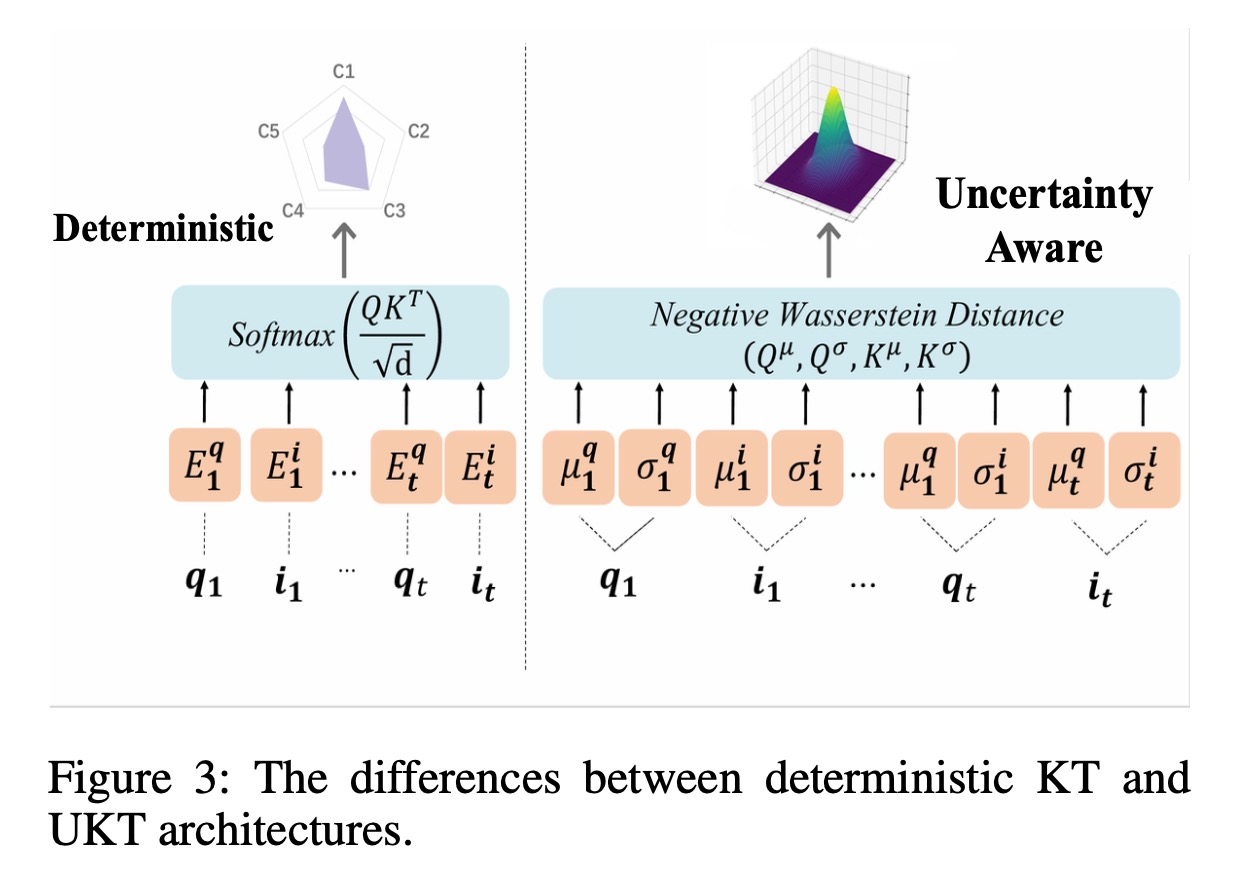
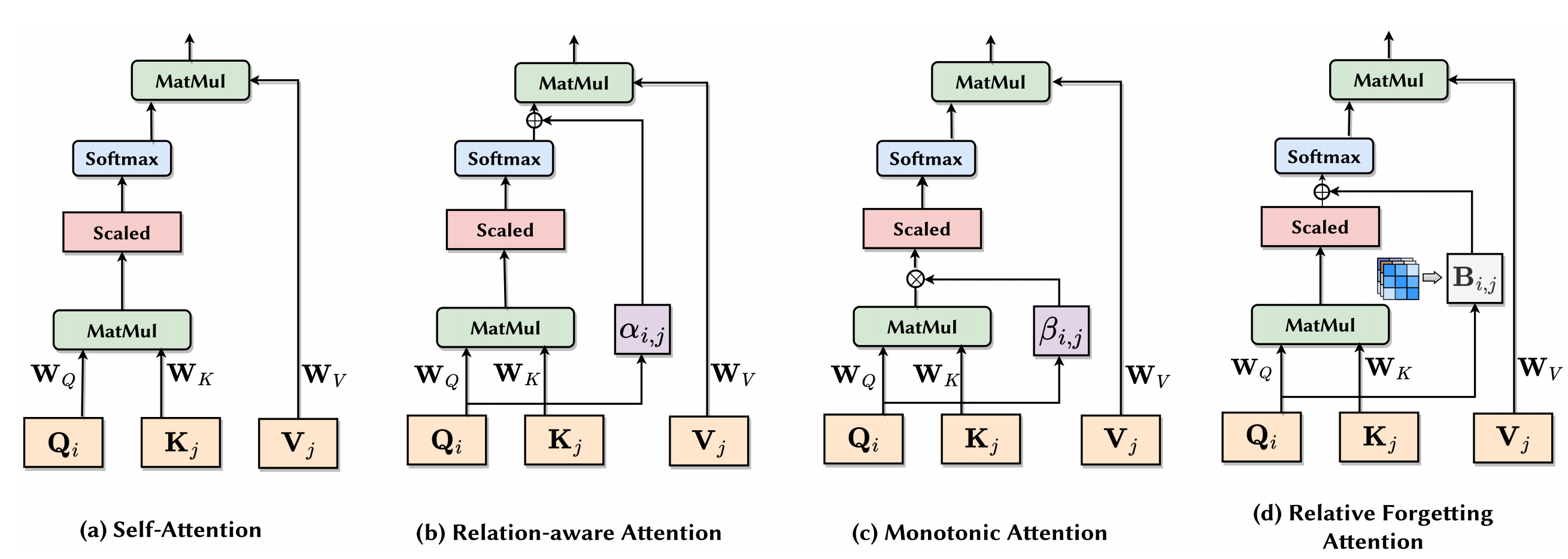
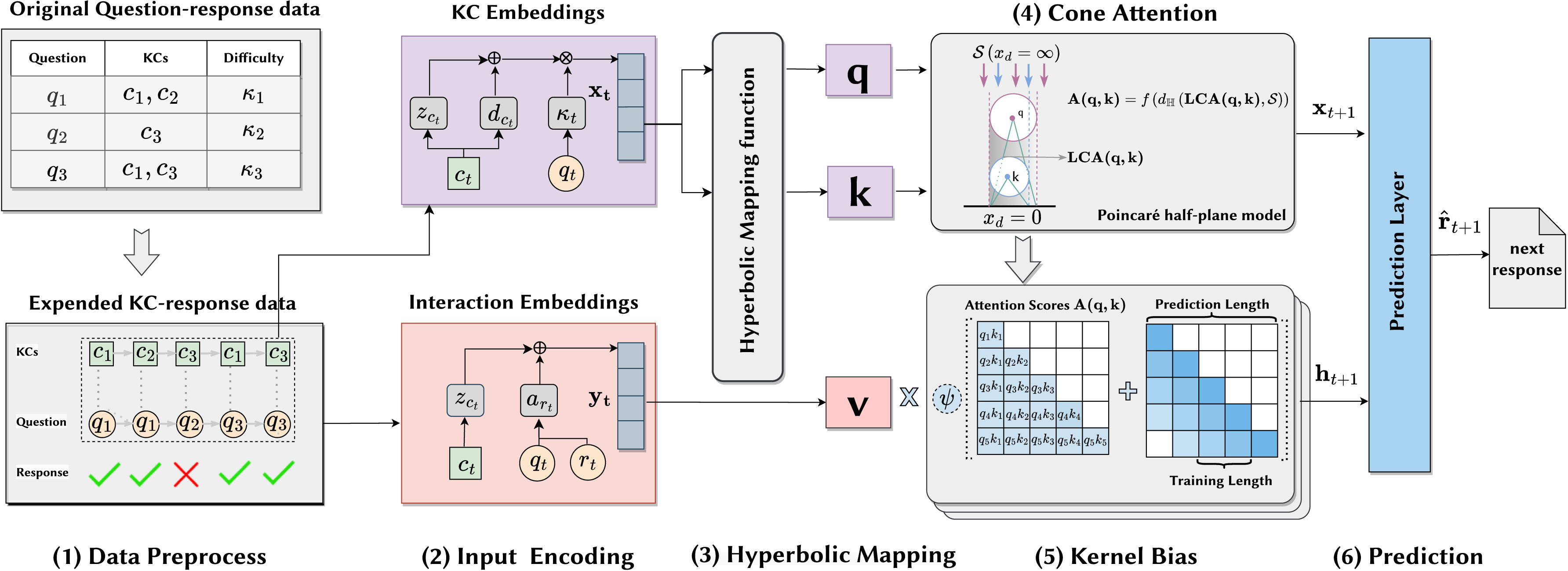
Abstract: Knowledge tracing (KT) involves using the historical recordsof student-learning interactions to anticipate their performance on forthcoming questions. Central to this process is the modeling of human cognition to gain deeper insights into how knowledge is acquired and retained. Human cognition is characterized by two key features: long-term cognitive trends, reflecting the gradual accumulation and stabilization of knowledge over time, and short-term cognitive fluctuations, which arise from transient factors such as forgetting or momentary lapses in attention. Although existing attention-based KT models effectively capture long-term cognitive trends, they often fail to adequately address short-term cognitive fluctuations. These limitations lead to overly smoothed cognitive features and reduced model performance, especially when the test data length exceeds the training data length. To address these problems, we propose FlucKT, a novel shortterm cognitive fluctuations enhanced attention network for KT tasks. FlucKT improves the attention mechanism in two ways: First, by using a decomposition-based layer with causal convolution to separate and dynamically reweight long-term and short-term cognitive features. Second, by introducing a kernelized bias attention score penalty to enhance focus on short-term fluctuations, improving length generalization capabilities. Our contributions are validated through extensive experiments on three real-world datasets, demonstrating significant improvements in length generalization and prediction performance.