Enhancing Knowledge Tracing through Decoupling Cognitive Pattern from Error-Prone Data
We added RoubstKT into our pyKT package.
The link is here and the API is here.
Original paper can be found at Guo,Teng et al. “Enhancing Knowledge Tracing through Decoupling Cognitive Pattern from Error-Prone Data.” The ACM on Web Conference. 2025.
Title: Enhancing Knowledge Tracing through Decoupling Cognitive Pattern from Error-Prone Data
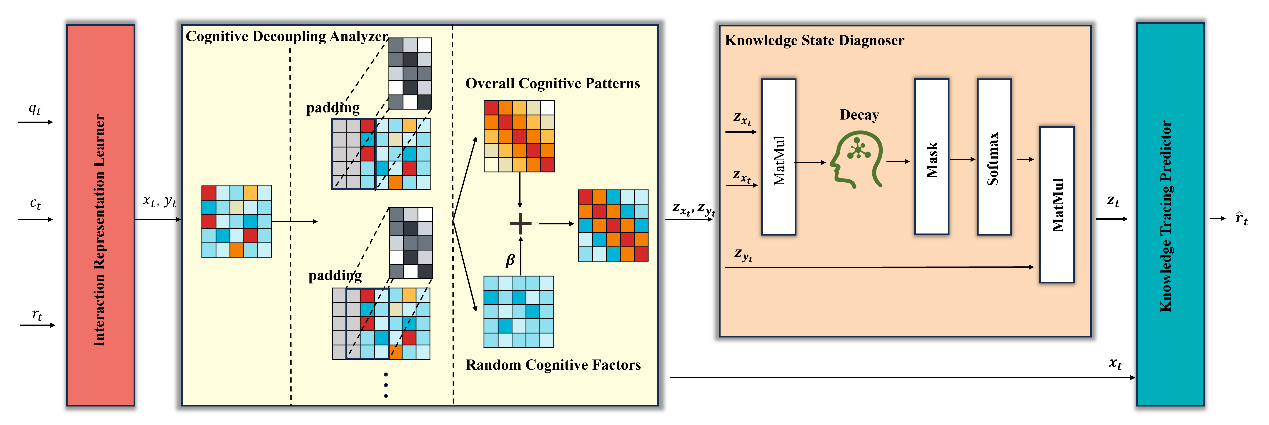
Abstract: Knowledge tracing aims to predict students’ future performance based on their past learning activities. However, no one is perfect. Factors such as carelessness, fatigue, and stress often cause students to make mistakes on problems they have already mastered, leading to anomalies in their historical learning data. These anomalies disrupt inherent patterns in the data, misleading the KT model. Extracting cognitive patterns that accurately reflect students’ knowledge mastery from such error-prone data remains a significant challenge. Against this background, this paper proposes a new knowledge tracing method named RoubstKT, inspired by educational measurement theory and frequency-based decomposition. A cognitive decoupling analyzer is proposed to decouple the student’s cognitive pattern and random factors from the data through smoothing and subtraction operations, then recombine them using a gating mechanism or adaptive parameter fusion strategy. To more effectively diagnose students’ knowledge mastery, we employ a decay-based attention mechanism that focuses on random behaviors at adjacent time steps. We conducted comprehensive experiments based on real-world datasets and targeted datasets with added random noise. The experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method.