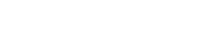Revisiting Knowledge Tracing: A Simple and Powerful Model
We added reKT into our pyKT package.
The link is here and the API is here.
Original paper can be found at Shen, Xiaoxuan, et al. “Revisiting Knowledge Tracing: A Simple and Powerful Model.” Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia. 2024.”.
Title: Revisiting Knowledge Tracing: A Simple and Powerful Model
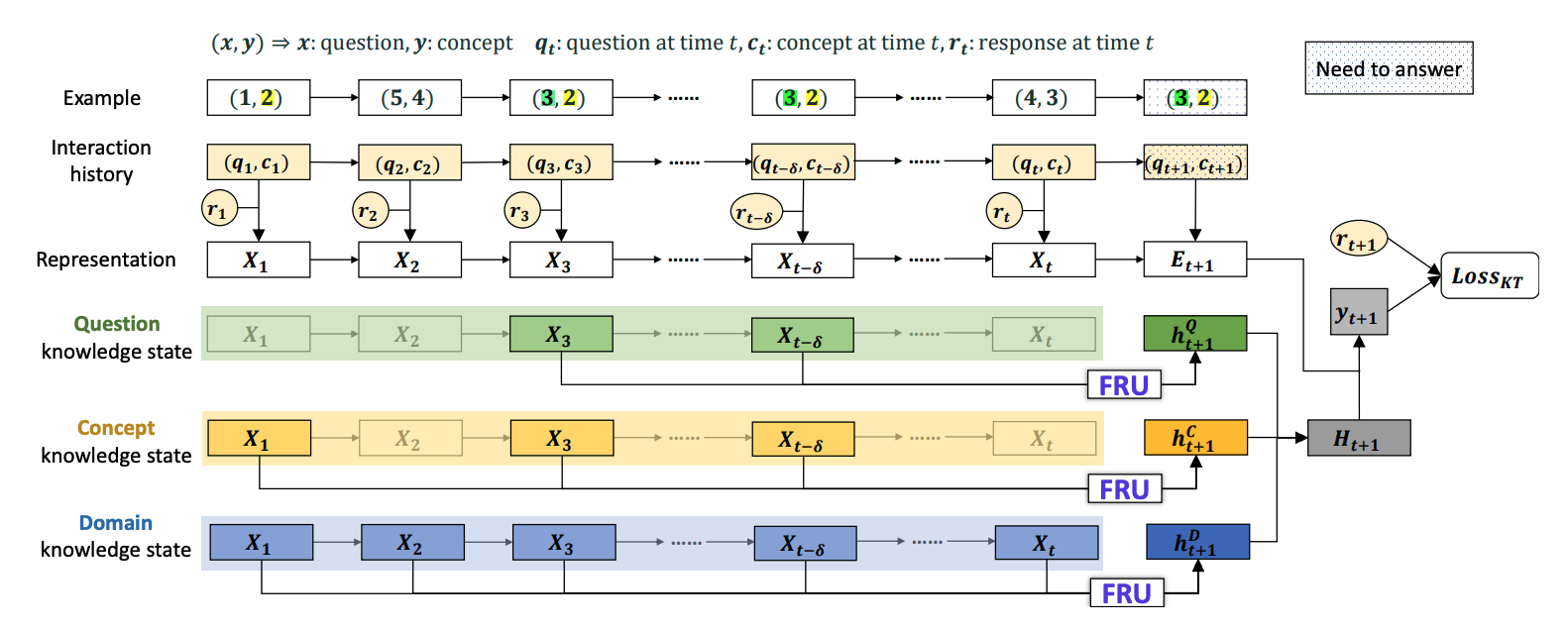
Abstract: Advances in multimedia technology and its widespread application in education have made multimedia learning increasingly important. Knowledge Tracing (KT) is the key technology for achieving adaptive multimedia learning, aiming to monitor the degree of knowledge acquisition and predict students’ performance during the learning process. Current KT research is dedicated to enhancing the performance of KT problems by integrating the most advanced deep learning techniques. However, this has led to increasingly complex models, which reduce model usability and divert researchers’ attention away from exploring the core issues of KT. This paper aims to tackle the fundamental challenges of KT tasks, including the knowledge state representation and the core architecture design, and investigate a novel KT model that is both simple and powerful. We have revisited the KT task and propose the ReKT model. First, taking inspiration from the decision-making process of human teachers, we model the knowledge state of students from three distinct perspectives: questions, concepts, and domains. Second, building upon human cognitive development models, such as constructivism, we have designed a Forget-Response-Update (FRU) framework to serve as the core architecture for the KT task. The FRU is composed of just two linear regression units, making it an extremely lightweight framework. Extensive comparisons were conducted with 22 state-of-the-art KT models on 7 publicly available datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that ReKT outperforms all the comparative methods in question-based KT tasks, and consistently achieves the best (in most cases) or near-best performance in concept-based KT tasks. Furthermore, in comparison to other KT core architectures like Transformers or LSTMs, the FRU achieves superior prediction performance with approximately only 38% computing resources. Through an exploration of the ReKT model that is both simple and powerful, is able to offer new insights to future KT research. The code can be found at https://github.com/lilstrawberry/ReKT.